 30. Wave interference
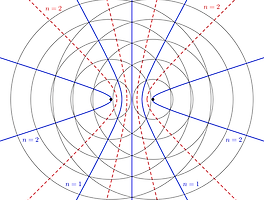
1. Wave interference 두 지점 A, B에서 각각 charge acceleration으로 인해 3차원적으로 spherical electromagnetic wave가 전파 될 때, 지점 P에서는 두 wave를 모두 수신할 수 있다.이 때, 3차원에서 wave는 amplitude가 거리에 반비례하게 감소하며 이동하게 되는데, P가 지점 A, B 보다 매우 멀리 떨어져 있을 경우 도달하는 wave의 amplitude의 차이는 거의 동일하게 된다.따라서, 지점P에서 phase가 180도 만큼 차이나는 wave끼리 마주칠 경우, 서로를 죽이게 된다. 이것을 destructive interference라고 한다. 이러한 사실들을 고려해 볼때, 동일한 wave를 지점1, 2에서 생성시켜 전파시킬 때,..
30. Wave interference
1. Wave interference 두 지점 A, B에서 각각 charge acceleration으로 인해 3차원적으로 spherical electromagnetic wave가 전파 될 때, 지점 P에서는 두 wave를 모두 수신할 수 있다.이 때, 3차원에서 wave는 amplitude가 거리에 반비례하게 감소하며 이동하게 되는데, P가 지점 A, B 보다 매우 멀리 떨어져 있을 경우 도달하는 wave의 amplitude의 차이는 거의 동일하게 된다.따라서, 지점P에서 phase가 180도 만큼 차이나는 wave끼리 마주칠 경우, 서로를 죽이게 된다. 이것을 destructive interference라고 한다. 이러한 사실들을 고려해 볼때, 동일한 wave를 지점1, 2에서 생성시켜 전파시킬 때,..